Lyme Disease Diagnosis in Veterinary Medicine

Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia mayonii, most commonly transmitted through the bite of infected ticks. This zoonotic infection can affect both humans and animals, with dogs being the most commonly impacted. Typical symptoms in dogs include joint swelling, fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite.
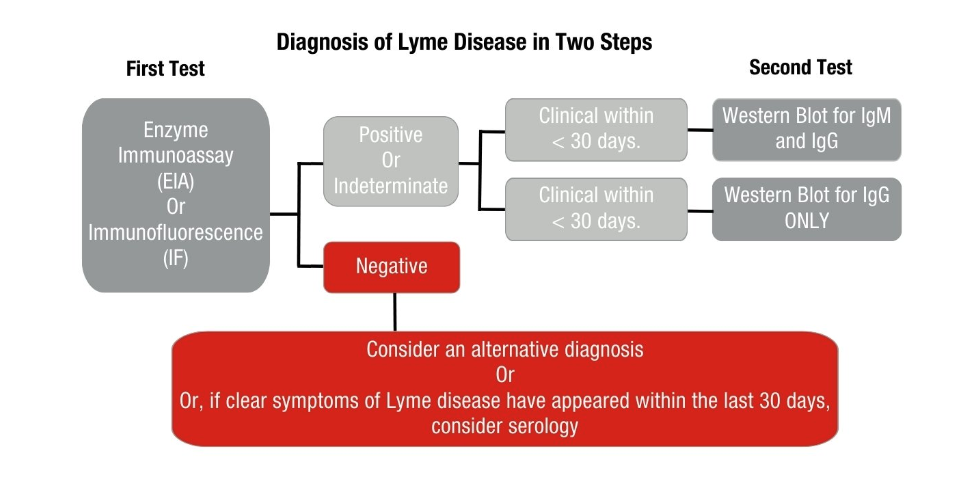
Detection and Analysis Process
The body’s immune system produces antibodies in response to exposure to the bacteria. Lyme disease tests measure the antibodies against Borrelia in the blood. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommend two types of tests for detection and diagnostic confirmation of Lyme disease: an immunoassay followed by a confirmatory Western Blot in the case of a positive result.
Collection and Isolation of Serum Antibodies for Diagnosis
The antibodies used in these tests are obtained from serum, which requires collecting a blood sample from the infected animal. This sample is drawn into a tube without anticoagulants and left to rest for about 30 minutes at room temperature to allow clot formation.
Subsequently, the sample is centrifuged at 1,500xG for 15 minutes at 4°C, causing the clot to precipitate due to its weight, leaving the serum containing the antibodies of interest in the supernatant.
Finally, to isolate the antibodies from the serum, sonication is initially used to break the cells, releasing both the internal antibodies and those bound to the cell membrane. The sample is then centrifuged at 1,500xG for 15 minutes at 4°C to separate the heavier cell debris (sedimented) from the lighter proteins of interest (remaining in the supernatant). Among these proteins are the antibodies, which will be analyzed in the corresponding test.
The Consul 22 R centrifuge is ideal for these centrifugation steps, offering optimal capacity and conditions for precise separations, as well as efficient temperature control that maintains the sample at 4°C, preserving the integrity of the antibodies and the quality of the serum.

Thus, serum antibody analysis is a simple and quick procedure, facilitated by centrifugation steps, which help optimize the process and ensure the proper separation of the sample’s elements.